UPX 4.0.2 源码分析
推荐 原创前言
因为最近一直在参加HW,在红队中学习到了很多新知识。加壳作为一个常用的免杀手段,我经常是知其然不知其所以然,因此打算自顶向下分析一下upx的源码,梳理整个程序运行的机制。本文将以最新版本 upx 4.0.2为基础,对 PE 64位程序加壳流程进行分析。
编译UPX
分析版本:upx-devel 4.0.2
需要压缩的程序:PE 64位程序
先对编译upx源码做一下记录,挺简单的,选择最新版本:
|
1
2
3
4
|
git clone https:
//github.com/upx/upx.git
cd upx
git submodule update --init
make all
|
生成的可执行文件upx在upx/build/release中。
目录结构分析
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
.
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── COPYING
├── LICENSE
├── Makefile
├── NEWS
├── README
├── README.SRC
├── compile_flags.txt
├── doc
│ ├── BUGS.txt
│ ├── Makefile
│ ├── THANKS.txt
│ ├── elf-to-mem.txt
│ ├── filter.txt
│ ├── linker.txt
│ ├── selinux.txt
│ ├── upx-doc.html
│ ├── upx-doc.txt
│ ├── upx.1
│ └── upx.pod
├── misc
│ ├── podman
│ ├── scripts
│ └── testsuite
├── src
│ ├── Makefile
│ ├── bele.h
│ ├── bele_policy.h
│ ├── check
│ ├── compress
│ ├── conf.h
│ ├── console
│ ├── except.cpp
│ ├── except.h
│ ├── file.cpp
│ ├── file.h
│ ├── filter
│ ├── filter.cpp
│ ├── filter.h
│ ├── headers.h
│ ├── help.cpp
...
...
|
doc 目录
在/doc中目前包含了elf-to-mem.txt,filter.txt,loader.txt,Makefile,selinux.txt,upx.pod几项。
elf-to-mem.txt说明了解压到内存的原理和条件filter.txt解释了UPX所采用的压缩算法和filter机制loader.txt告诉开发者如何自定义 loaderselinux.txt介绍了SE Linux中对内存匿名映像的权限控制给UPX造成的影响。这部分文件适用于想更加深入了解UPX的研究者和开发者upx.pod是含关于 UPX 使用方法和功能详解的文档,转换为了upx-doc.html和upx-doc.txt
src 目录
我UPX源码都在文件夹/src中,进入该文件夹后我们可以发现其源码由文件夹/src/check,/src/compress,/src/console,/src/filter,/src/stub,/util和一系列*.h, *.cpp文件构成。
/src/check:此处代码主要是为了检查编译时和运行时环境是否能支持 UPX 的要求,找到潜在的兼容性问题/src/compress:主要包含了压缩的算法/src/console:这里的代码主要是实现 UPX 在 Windows 的控制台驱动,使其能像在 linux terminal 那样交互。/src/filter:是一系列被filter机制和UPX使用的头文件。/src/stub:包含了针对不同平台,架构和格式的文件头定义和loader源码,loader源码在src/stub/src/中,对应不同架构。/util:这里的代码负责安全性,进行内存管理,帮助发现和避免一些内存错误之类的。例如里面的xspan.cpp文件,其中:XSpanStats结构体:它记录了各种类型的异常情况的计数器,例如空指针、空基址以及和基址不匹配的指针等。xspan_fail_*函数:这些函数被用来处理各种失败的情况,例如空指针、空基址或者和基址不匹配的指针。当这些情况发生时,相应的计数器会增加,并抛出一个错误。xspan_check_range函数:这个函数接受一个指针、一个基础地址以及一个大小值(以字节为单位)。它首先检查指针和基地址是否为空,然后检查指针是否在从基地址开始的给定大小的范围内。如果任何检查失败,它将调用相应的 xspan_fail_* 函数来处理。
- 其余的代码文件主要可以分为负责UPX程序总体的
main.cpp,work.cp和packmast.cpp,负责加脱壳类的定义与实现的p_*.h和p_*.cpp,以及其他起到显示,运算等辅助作用的源码文件。
我们的分析将会从main.cpp入手,经过work.cpp,最终跳转到对应架构和平台的packer()类中。
源码分析
整个源码运行流程如下:
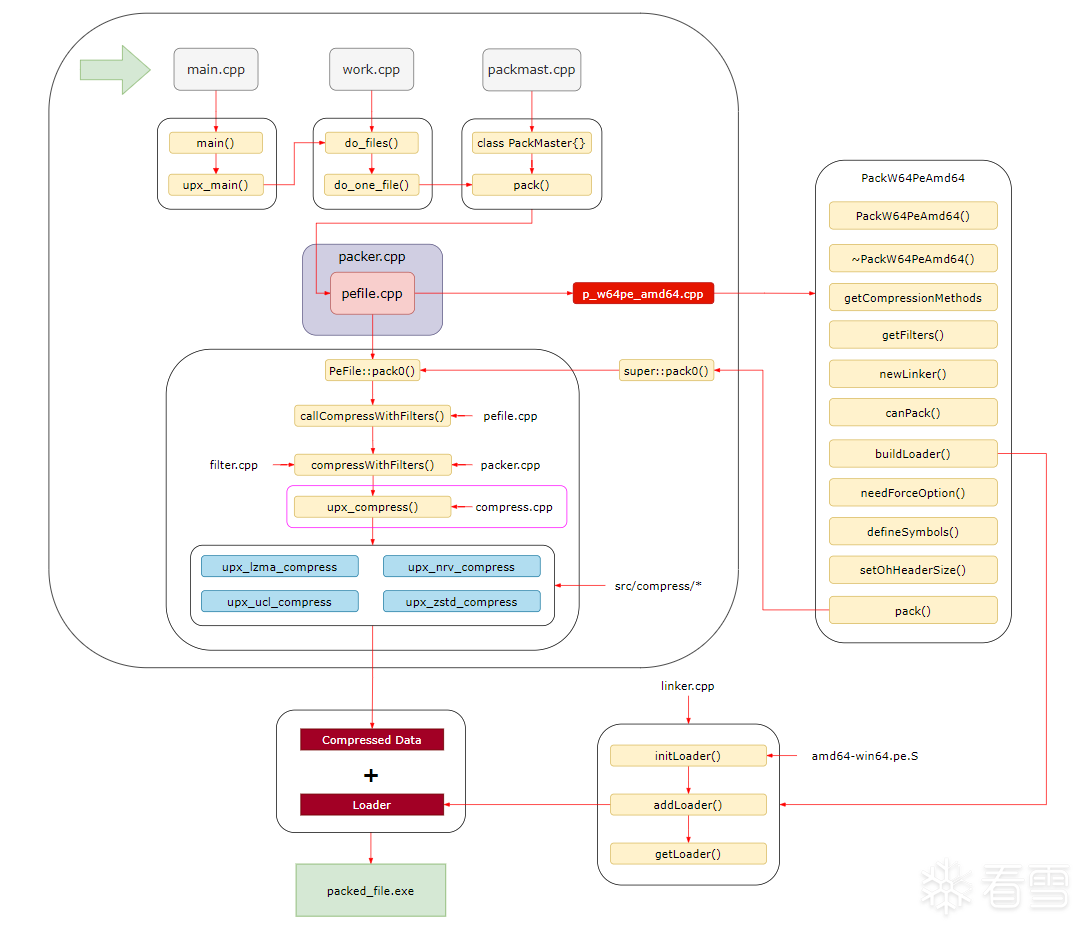
main.cpp
main 函数
main.cpp 包含的函数功能:
main():主函数upx_main():主入口函数main_get_options():获取参数main_get_envoptions():从环境变量获取参数check_options():检查参数catch异常并退出
我们先从主函数入手,可以看到主函数main()的主要作用是调用upx_main():
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
int
__acc_cdecl_main main(
int
argc,
char
*argv[]) {
#if 0 && (ACC_OS_DOS32) && defined(__DJGPP__)
// LFN=n may cause problems with 2.03's _rename and mkdir under WinME
putenv(
"LFN=y"
);
#endif
#if (ACC_OS_WIN32 || ACC_OS_WIN64) && (ACC_CC_MSC) && defined(_WRITE_ABORT_MSG) && \
defined(_CALL_REPORTFAULT)
_set_abort_behavior(_WRITE_ABORT_MSG, _WRITE_ABORT_MSG | _CALL_REPORTFAULT);
#endif
acc_wildargv(&argc, &argv);
// srand((int) time(nullptr));
srand
((
int
)
clock
());
// info: main() is implicitly "noexcept", so we need a try block
#if 0
int
r = upx_main(argc, argv);
#else
int
r;
try
{
r = upx_main(argc, argv);
}
catch
(
const
Throwable &e) {
printErr(
"unknown"
, e);
std::terminate();
}
catch
(...) {
std::terminate();
}
#endif
#if 0 && defined(__GLIBC__)
// malloc_stats();
#endif
return
r;
}
|
__acc_cdecl_main 这个函数修饰符是为了确保 main 函数使用正确的调用约定。具体来说不同的编译器可能有不同的默认调用约定:
- GCC 和 Clang 的默认是
__attribute__((cdecl)), 等价于 cdecl。 - MSVC 的默认是 __stdcall 。
为了可移植性,UPX 定义了 __acc_cdecl_main 函数修饰符,当编译 UPX 时:
- 对于 GCC/Clang,
__acc_cdecl_main为空,main 正常定义。 - 对于 MSVC,通过 __cdecl 定义 main ,强制用 cdecl 调用约定。
|
1
2
3
4
|
#if (ACC_OS_WIN32 || ACC_OS_WIN64) && (ACC_CC_MSC) && defined(_WRITE_ABORT_MSG) && \
defined(_CALL_REPORTFAULT)
_set_abort_behavior(_WRITE_ABORT_MSG, _WRITE_ABORT_MSG | _CALL_REPORTFAULT);
#endif
|
如果操作系统是 Windows 并使用 MSVC 编译器,且定义了_WRITE_ABORT_MSG 和 _CALL_REPORTFAULT 宏,就会执行:_set_abort_behavior(_WRITE_ABORT_MSG, _WRITE_ABORT_MSG | _CALL_REPORTFAULT);
这行代码用来设置 Crash 时的行为,启用 Crash 日志和报告功能。
|
1
|
acc_wildargv(&argc, &argv);
|
根据命名我推测这行代是用来码处理 wildcards 参数的,wildcards(Windows wildcards) 指的是 Windows 中的通配符:
- 检查是否存在通配符
- 如果存在,则展开通配符,获得实际的参数列表
- 更新 argc 和 argv ,指向新的参数列表
总的来说这个函数的功能为:根据通配符acc_wildargv()函数会操作和修改命令行参数acc_wildargv的声明是在miniacc.h文件中:
|
1
|
ACCLIB_EXTERN(
void
, acc_wildargv) (
int
*,
char
***);
|
宏 ACCLIB_EXTERN 的定义是:
|
1
|
#define ACCLIB_EXTERN(rt,func,args) rt func args
|
就是简单地展开成一个标准的函数声明:
|
1
|
void
acc_wildargv(
int
*argc,
char
***argv);
|
它的作用是:
- 向使用这个头文件的代码提供 acc_wildargv() 的函数声明
- 隐藏具体的 AccLib 命名空间,只暴露标准的函数声明
这样可以在不泄露实现的情况下,向其他代码提供 AccLib 中函数的接口。
接着往下看main代码,可以看到:
|
1
|
srand
((
int
)
clock
());
|
这里是初始化随机数发生器,srand的工作模式为:
- 第一次调用 srand() 时,使用指定的种子初始化随机数发生器
- 之后每调用一次 rand(),从随机数发生器中产生下一个随机数
如果想看一下这个随机函数用在了哪些地方,具体可以看一下packer.cpp中用到的rand():
第一个用到的地方是用来生成打包文件的随机 ID,这个随机 ID 用来区分不同的打包文件。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
// Create a pseudo-unique program id.
unsigned Packer::getRandomId()
const
{
if
(opt->debug.disable_random_id)
return
0x01020304;
unsigned id = 0;
#if 0 && defined(__unix__)
// Don't consume precious bytes from /dev/urandom.
int
fd = open(
"/dev/urandom"
, O_RDONLY | O_BINARY);
if
(fd < 0)
fd = open(
"/dev/random"
, O_RDONLY | O_BINARY);
if
(fd >= 0) {
if
(read(fd, &id, 4) != 4)
id = 0;
close(fd);
}
#endif
while
(id == 0) {
#if !(HAVE_GETTIMEOFDAY) || ((ACC_OS_DOS32) && defined(__DJGPP__))
id ^= (unsigned)
time
(nullptr);
id ^= ((unsigned)
clock
()) << 12;
#else
struct
timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, nullptr);
id ^= (unsigned) tv.tv_sec;
id ^= ((unsigned) tv.tv_usec) << 12;
// shift into high-bits
#endif
#if HAVE_GETPID
id ^= (unsigned) getpid();
#endif
id ^= (unsigned) fi->st.st_ino;
id ^= (unsigned) fi->st.st_atime;
id ^= (unsigned)
rand
();
}
return
id;
}
|
第二个地方是在调试模式下随机选择一个压缩方法或过滤器(Filter):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
if
(opt->debug.use_random_method && nmethods >= 2) {
int
method = methods[
rand
() % nmethods];
...
}
if
(opt->debug.use_random_filter && nfilters >= 3 && filters[nfilters - 1] == 0) {
int
filter_id = filters[
rand
() % (nfilters - 1)];
...
}
|
这里提前讲一下 filter,过滤器(Filter)是 UPX 中用于预处理输入文件的数据流的组件,它可以实现一些转换,从而改善输入数据的压缩效果。
过滤器能够预处理输入流从而给予压缩算法更好的输入,Packer 会尝试使用不同的过滤器并选择压缩效果最好的那个。
main函数主要还是去执行upx_main()的,接着看upx_main()。
upx_main 函数
upx_main() 函数具体流程为:
- 进行命令行参数解析初始化、压缩算法初始化、随机数初始化、版本信息初始化等
- 调用upx_doctest_check()做一些doctest测试
- 解析命令行参数opt,读取配置
- 根据命令执行不同处理:压缩、解压、显示信息等
- 如果是压缩或解压命令,会调用do_files()
- do_files()会循环处理每个文件,调用do_one_file()
- do_one_file()会创建PackMaster实例,并调用其pack/unpack方法
- PackMaster会根据格式创建Packer子类实例,如PeFile
- PeFile中的pack/unpack方法会进行实际的压缩/解压处理
- 在压缩处理中,会调用PeFile的compressWithFilters()方法
- compressWithFilters()会创建Filter实例,并调用其过滤处理数据
首先在完成初始化后,调用main_get_options() 解析命令行参数,根据参数设置 opt 全局配置,根据 opt->cmd决定执行哪个操作,默认为压缩。接着开始压缩工作,调用 do_files() 压缩/解压缩传入的文件列表(do_files()具体函数声明在work.cpp中),返回操作结果。opt->cmd 是 UPX 源码中一个全局变量,表示需要执行的操作。代码定义在 src/options.h 中:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
/*************************************************************************
// command line options
**************************************************************************/
// main command
enum
{
CMD_NONE,
CMD_COMPRESS,
CMD_DECOMPRESS,
CMD_TEST,
CMD_LIST,
CMD_FILEINFO,
CMD_HELP,
CMD_LICENSE,
CMD_VERSION,
};
struct
Options;
extern
Options *opt;
// global options, see class PackMaster for per-file local options
struct
Options final {
int
cmd;
// compression options
int
method;
bool
method_lzma_seen;
bool
method_nrv2b_seen;
bool
method_nrv2d_seen;
bool
method_nrv2e_seen;
int
level;
// compression level 1..10
int
filter;
// preferred filter from Packer::getFilters()
bool
ultra_brute;
bool
all_methods;
// try all available compression methods ?
int
all_methods_use_lzma;
bool
all_filters;
// try all available filters ?
bool
no_filter;
// force no filter
bool
prefer_ucl;
// prefer UCL
bool
exact;
// user requires byte-identical decompression
....
}
|
opt -> cmd中opt 是 Options 结构体的一个指针,含义为访问结构体 Options 的成员(成员变量) cmd,cmd成员包含的值如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
enum
{
CMD_NONE,
CMD_COMPRESS,
// 压缩
CMD_DECOMPRESS,
// 解压缩
CMD_TEST,
// 测试
CMD_LIST,
// 列出文件内容
CMD_FILEINFO,
// 查看文件信息
CMD_HELP,
// 显示帮助信息
CMD_LICENSE,
// 显示软件许可
CMD_VERSION,
// 显示版本信息
};
|
在upx_main()函数中,根据解析到的命令行参数会设置opt->cmd为对应的操作值:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
switch
(opt->cmd) {
case
CMD_COMPRESS:
//...
break
;
case
CMD_DECOMPRESS:
//...
break
;
// ...
}
|
接着看开始工作部分,/* start work */代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
/* start work */
set_term(stdout);
if
(do_files(i, argc, argv) != 0)
return
exit_code;
if
(gitrev[0]) {
// also see UPX_CONFIG_DISABLE_GITREV in CMakeLists.txt
bool
warn_gitrev =
true
;
const
char
*ee =
getenv
(
"UPX_DEBUG_DISABLE_GITREV_WARNING"
);
if
(ee && ee[0] &&
strcmp
(ee,
"1"
) == 0)
warn_gitrev =
false
;
if
(warn_gitrev) {
FILE
*f = stdout;
int
fg = con_fg(f, FG_RED);
con_fprintf(
f,
"\nWARNING: this is an unstable beta version - use for testing only! Really.\n"
);
fg = con_fg(f, fg);
UNUSED(fg);
}
}
|
do_files() 函数的功能是处理命令行传入的多个文件,函数声明在work.cpp中,相对应work.cpp中有处理单一文件的函数do_one_file(),多文件时使用do_files()先初步处理,然后再让do_one_file()挨个根据opt->cmd 执行不同的操作:
- 如果 opt->cmd 是 CMD_COMPRESS ,则对每个文件调用 do_one_file() 压缩
- 如果 opt->cmd 是 CMD_DECOMPRESS ,则对每个文件调用 do_one_file() 解压缩
- 在处理每个文件时,能够处理异常,返回相应的错误码。
- 在处理完成所有文件后,调用 UiPacker 的相应函数,提供总结信息(UiPacker负责UPX中和用户交互相关的所有功能,包括进度显示、交互事件、统计信息收集等)
- 返回 0 表示成功处理所有文件,返回 -1 表示有一个文件处理时出现致命错误。
do_one_file() 函数的具体操作流程:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
void
do_one_file(
const
char
*iname,
char
*oname) {
int
r;
struct
stat st;
mem_clear(&st);
#if HAVE_LSTAT
r = lstat(iname, &st);
#else
r = stat(iname, &st);
...
}
|
- 打开输入文件(iname)并获取文件信息,如大小、权限等
- 检查文件是否为普通文件,并且大小大于零
- 打开输出文件(oname),可以是一个文件或者标准输出
- 根据 opt->cmd 的值,调用PackMaster执行不同的操作:
- 如果 opt->cmd 是 CMD_COMPRESS ,则调用 pm.pack() 对文件进行压缩
- 如果opt->cmd 是 CMD_DECOMPRESS ,则调用 pm.unpack() 对文件进行解压缩
- 如果需要,则复制输入文件的时间戳等属性到输出文件,然后关闭输入输出文件
- 如果生成了临时输出文件,则保留输出文件并删除输入文件(即完成重命名),或者生成备份并删除输入文件
- 处理异常,抛出相应的异常或错误
此处pm是PackMaster的对象:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
// handle command - actual work is here
PackMaster pm(&fi, opt);
if
(opt->cmd == CMD_COMPRESS)
pm.pack(&fo);
else
if
(opt->cmd == CMD_DECOMPRESS)
pm.unpack(&fo);
else
if
(opt->cmd == CMD_TEST)
pm.test();
else
if
(opt->cmd == CMD_LIST)
pm.list();
else
if
(opt->cmd == CMD_FILEINFO)
pm.fileInfo();
else
throwInternalError(
"invalid command"
);
|
PackMaster 类的定义在 src/packmast.h 中,注释写得十分清楚:"dispatch to a concrete subclass of class Packer; see work.cpp",这个部分后面会讲。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
#pragma once
class
Packer;
class
InputFile;
class
OutputFile;
/*************************************************************************
// dispatch to a concrete subclass of class Packer; see work.cpp
**************************************************************************/
class
PackMaster final {
public
:
explicit
PackMaster(InputFile *f, Options *o = nullptr) noexcept;
~PackMaster() noexcept;
void
pack(OutputFile *fo);
void
unpack(OutputFile *fo);
void
test();
void
list();
void
fileInfo();
typedef
Packer *(*visit_func_t)(Packer *p,
void
*user);
static
Packer *visitAllPackers(visit_func_t, InputFile *f,
const
Options *,
void
*user);
private
:
OwningPointer(Packer) packer = nullptr;
// owner
InputFile *fi = nullptr;
// reference
static
Packer *getPacker(InputFile *f);
static
Packer *getUnpacker(InputFile *f);
// setup local options for each file
Options local_options;
Options *saved_opt = nullptr;
};
/* vim:set ts=4 sw=4 et: */
|
PackMaster 类的主要功能是:
- PackMaster 的构造函数会调用 getPacker() 函数,根据输入文件的类型分配对应的 Packer 子类。
- pack()、unpack() 等函数,实际上是通过 packer 属性调用对应的 Packer 子类的方法。
- local_options 是个 Options 结构体,它存储了独立于全局配置的选项。
PackMaster 可以在不修改 Packer 子类的情况下,支持不同的文件类型,这也是packmast.cpp的主要功能。虽然 PackMaster 使用了 final 关键字,让这个类不会再有子类,但是 PackMaster 类内部引用了 Packer 类,Packer 类的声明位于 packer.h 中,通过这个 Packer 子类对象再执行不同的操作。
packmast.cpp
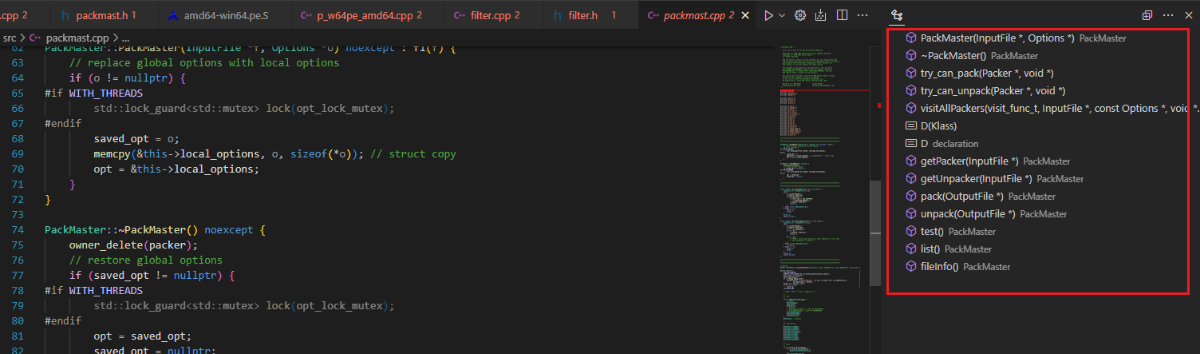
packmast.cpp在整个upx加壳流程中起到了分类的作用,其中getPacker()会根据文件格式选择合适的打包器类,比如说检测到PE文件则选择pefile.cpp。下面详细说明packmast.cpp实现的功能:
在packmast.h中声明了PackMaster类,后续work.cpp会用到这个类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
/*************************************************************************
// dispatch to a concrete subclass of class Packer; see work.cpp
**************************************************************************/
class
PackMaster final {
public
:
explicit
PackMaster(InputFile *f, Options *o = nullptr) noexcept;
~PackMaster() noexcept;
void
pack(OutputFile *fo);
void
unpack(OutputFile *fo);
void
test();
void
list();
void
fileInfo();
typedef
Packer *(*visit_func_t)(Packer *p,
void
*user);
static
Packer *visitAllPackers(visit_func_t, InputFile *f,
const
Options *,
void
*user);
private
:
OwningPointer(Packer) packer = nullptr;
// owner
InputFile *fi = nullptr;
// reference
static
Packer *getPacker(InputFile *f);
static
Packer *getUnpacker(InputFile *f);
// setup local options for each file
Options local_options;
Options *saved_opt = nullptr;
};
/* vim:set ts=4 sw=4 et: */
|
在packmast.cpp中代码一开始使用构造函数PackMaster::PackMaster(InputFile *f, Options *o) noexcept : fi(f)来初始化PackMaster对象的状态。PackMaster类的实现提供了以下功能:
PackMaster::PackMaster:PackMaster类的构造器接受一个InputFile的指针和一个可选的Options指针。如果提供了Options,它会创建一个该选项的本地副本,并将全局的opt指针设置为指向这个本地副本。这样,PackMaster对象就可以使用自己的选项,而不影响全局的选项。析构器则在PackMaster对象被销毁时恢复全局的opt选项并删除packer对象。pack():用于执行压缩操作。它首先获取一个适合输入文件的Packer对象,然后调用该对象的doPack()方法来进行压缩。unpack():用于执行解压缩操作。它首先获取一个适合输入文件的Packer对象,然后调用该对象的doUnpack()方法来进行解压缩。test():用于测试已压缩的文件。它首先获取一个适合输入文件的Packer对象,然后调用该对象的doTest()方法来进行测试。list():用于列出已压缩文件的信息。它首先获取一个适合输入文件的Packer对象,然后调用该对象的doList()方法来进行列出。fileInfo():用于获取文件信息。它首先尝试获取一个适合解压缩输入文件的Packer对象,如果失败,再尝试获取一个适合压缩输入文件的Packer对象,然后调用该对象的doFileInfo()方法来获取文件信息。visitAllPackers():这个方法遍历所有可能的Packer类型,并对每个类型执行给定的函数。这个函数(try_can_pack或try_can_unpack)会检查该类型的Packer是否可以处理给定的输入文件。如果可以,那么该Packer对象就会被返回。getPacker()和getUnpacker():这两个方法都使用visitAllPackers()方法来找到一个适合处理输入文件的Packer对象。getPacker()找到的是可以压缩输入文件的Packer,而getUnpacker()找到的是可以解压缩输入文件的Packer。
work.cpp
该源码从上到下包含的主要函数有三个:
- do_files:这个函数处理从命令行传入的所有文件。它首先进行编译器的一致性检查,然后遍历所有输入的文件,对每个文件调用do_one_file进行处理,捕获并处理可能抛出的异常。在处理所有文件后,根据命令调用UiPacker的相应函数进行输出。
- do_one_file:这个函数负责处理一个文件。主要步骤包括检查文件属性(是否是普通文件,文件大小是否合理,权限是否合理等),打开输入文件,打开或者创建输出文件,根据命令(压缩,解压缩,测试,列出,获取文件信息)调用PackMaster进行处理,复制时间戳,关闭文件,根据需要更改文件名或者删除文件,复制文件属性。
- unlink_ofile:这个函数负责在发生异常时删除输出文件。unlink_ofile 在 do_one_file 和 do_files 内部使用,不导出。
这个地方的代码主要是根据packmast.cpp提供的PackMaster类构造PackMaster对象,例如下面的代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
InputFile fi;
fi.st = st;
fi.sopen(iname, O_RDONLY | O_BINARY, SH_DENYWR);
...
// handle command - actual work is here
PackMaster pm(&fi, opt);
if
(opt->cmd == CMD_COMPRESS)
pm.pack(&fo);
else
if
(opt->cmd == CMD_DECOMPRESS)
pm.unpack(&fo);
else
if
(opt->cmd == CMD_TEST)
pm.test();
else
if
(opt->cmd == CMD_LIST)
pm.list();
else
if
(opt->cmd == CMD_FILEINFO)
pm.fileInfo();
else
throwInternalError(
"invalid command"
);
|
这段代码首先创建了一个 InputFile 对象 fi,并打开了输入文件 iname,接着创建一个名为 fo 的 OutputFile 对象,然后使用这个输入文件 fi 和选项 opt,创建了一个 PackMaster 对象 pm。如果选项 opt 指定的命令是压缩 (CMD_COMPRESS),那么就调用 pm 的 pack 方法,并传入输出文件对象 fo进行压缩操作。
work.cpp与pefile.cpp的关系是什么?
- work.cpp中的do_one_file()会调用PackMaster进行单个文件的压缩处理。
- PackMaster会根据文件类型创建合适的Packer子类实例,比如PeFile。
- PeFile定义了pack()和unpack()方法实现具体的压缩和解压。
- work.cpp最终通过PackMaster调用到PeFile的pack()方法实现对PE文件的压缩。
- PeFile::pack()会调用各过程完成导入表、重定位等处理,并调用compressWithFilters()进行实际压缩。
- 压缩结果会写入输出文件,完成整个压缩过程。
- 对解压也是类似的过程,work.cpp通过PackMaster调用PeFile::unpack()。
所以 work.cpp 控制总体流程,使用 packmast.cpp 来根据文件类型从 packer.cpp 中选择 PeFile 来实现特定格式PE文件的处理。
packer.cpp
packer.cpp 实现了 Packer 抽象类的具体函数,用来提供不同文件格式的打包和解包的基类。Packer 是 PackMaster 的子类,再作为 pefile.cpp 的基类,后续 pefile.cpp 会继承 packer.cpp 的一部分特性进行打包。
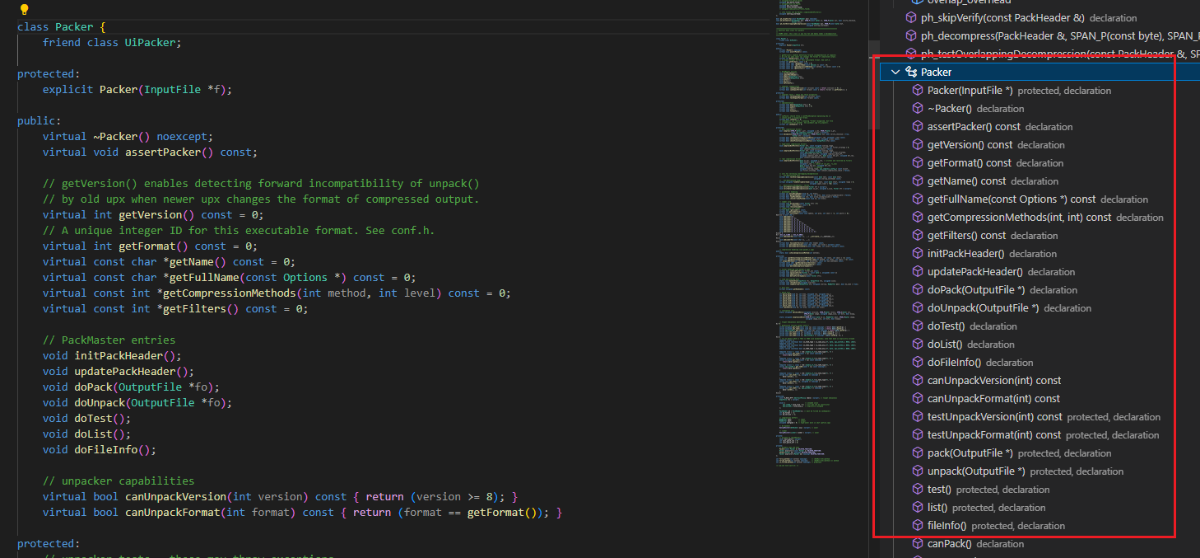
Packer 抽象类提供了共享的函数,子类可以实现各自的压缩和解压算法。在源码里我们可以看到还有packer_f.cpp、packer_c.cpp、packer_c.cpp,这些文件提供了基于packer.cpp函数的共享函数,例如 packer_c.cpp 提供了的共享函数:
|
1
2
3
|
isValidCompressionMethod()
getDefaultCompressionMethods()
getDecompressorSections()
|
这些函数并不是 packer.cpp 类的内部函数,而是可以被 Packer 子类调用的共享函数。例如下面我们要讲到的 PeFile 可以这样使用:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
class
PeFile:
public
Packer {
void
compress() {
methods = getDefaultCompressionMethods();
// 调用共享函数
// ...
}
}
|
在packer.cpp中packer_c.cpp提供的isValidCompressionMethod()也是直接使用的:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
int
Packer::prepareMethods(
int
*methods,
int
ph_method,
const
int
*all_methods)
const
{
int
nmethods = 0;
if
(!opt->all_methods || all_methods == nullptr || (-0x80 == (ph_method >> 24))) {
methods[nmethods++] = forced_method(ph_method);
return
nmethods;
}
for
(
int
mm = 0; all_methods[mm] != M_END; ++mm) {
int
method = all_methods[mm];
if
(method == M_ULTRA_BRUTE && !opt->ultra_brute)
break
;
if
(method == M_SKIP || method == M_ULTRA_BRUTE)
continue
;
if
(opt->all_methods && opt->all_methods_use_lzma != 1 && M_IS_LZMA(method))
continue
;
// check duplicate
assert
(Packer::isValidCompressionMethod(method));
// 此处使用assert检查是否true, 如果false就会抛出assertion failed错误
// assert 语句仅在调试环境下有效,在发布版本(Release mode)中 assert 语句会被自动忽略
for
(
int
i = 0; i < nmethods; i++)
assert
(method != methods[i]);
// use this method
methods[nmethods++] = method;
}
// debug
if
(opt->debug.use_random_method && nmethods >= 2) {
int
method = methods[
rand
() % nmethods];
methods[0] = method;
nmethods = 1;
NO_printf(
"\nuse_random_method = %d\n"
, method);
}
return
nmethods;
}
|
在压缩过程中最主要的是void Packer::compressWithFilters(),packer.cpp使用重载对这个函数进行了封装:
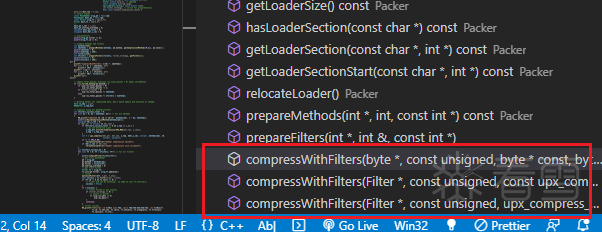
compressWithFilters 函数是用来找到最佳的压缩方法和过滤器,并执行实际的压缩操作的一个核心函数。下面是这个函数的主要步骤:
- 初始化:函数首先备份原始的 PackHeader 和 Filter 对象,然后设置一些初始的最佳压缩结果。
- 准备压缩方法和过滤器:函数调用 prepareMethods 和 prepareFilters 函数来获取需要尝试的所有压缩方法和过滤器。
- 尝试各种压缩方法和过滤器:函数遍历所有压缩方法和过滤器的组合。对于每一种组合,它会首先备份原始的 PackHeader 和 Filter 对象,然后尝试应用过滤器和压缩方法。如果过滤器和压缩方法都成功,并且得到的压缩结果比当前的最佳结果更好,那么就更新最佳结果。
- 恢复数据:对每一种压缩方法和过滤器的组合,尝试完成后,函数会恢复原始的数据,以便于下一次尝试。
- 检查压缩结果:在所有的压缩方法和过滤器都尝试完毕后,函数会检查得到的最佳压缩结果。如果压缩后的数据大小没有比原始数据小,那么就抛出一个异常,表示数据不能被压缩。
- 保存结果:最后,函数会将得到的最佳压缩结果保存到 Packer 对象的 ph 成员(一个 PackHeader 对象)和 parm_ft 参数指向的 Filter 对象中,最后执行
buildLoader(&best_ft);来构造一个合适的加载器,这个加载器会被嵌入到压缩的可执行文件中,用来在运行时解压和恢复原始的程序。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
// copy back results
this
->ph = best_ph;
*parm_ft = best_ft;
// Finally, check compression ratio.
// Might be inhibited when blocksize < file_size, for instance.
if
(!inhibit_compression_check) {
if
(best_ph.c_len + best_ph_lsize >= best_ph.u_len)
throwNotCompressible();
if
(!checkCompressionRatio(best_ph.u_len, best_ph.c_len))
throwNotCompressible();
// postconditions 2)
assert
(best_ph.overlap_overhead > 0);
}
// convenience
buildLoader(&best_ft);
|
pefile.cpp
pefile.cpp 是 packer.cpp 的子类,主要是针对PE文件进行操作。在压缩过程中我们需要注意PeFile::pack0函数。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
|
template
<
typename
ht,
typename
LEXX,
typename
ord_mask_t>
void
PeFile::unpack0(OutputFile *fo,
const
ht &ih, ht &oh, ord_mask_t ord_mask,
bool
set_oft) {
// infoHeader("[Processing %s, format %s, %d sections]", fn_basename(fi->getName()), getName(),
// objs);
handleStub(fi, fo, pe_offset);
if
(ih.filealign == 0)
throwCantUnpack(
"unexpected value in the PE header"
);
const
unsigned iobjs = ih.objects;
const
unsigned overlay =
file_size_u -
ALIGN_UP(isection[iobjs - 1].rawdataptr + isection[iobjs - 1].size, ih.filealign);
checkOverlay(overlay);
ibuf.alloc(ph.c_len);
obuf.allocForDecompression(ph.u_len);
fi->seek(isection[1].rawdataptr - 64 + ph.buf_offset + ph.getPackHeaderSize(), SEEK_SET);
fi->readx(ibuf, ibufgood = ph.c_len);
// decompress
decompress(ibuf, obuf);
unsigned skip = get_le32(obuf + (ph.u_len - 4));
unsigned take =
sizeof
(oh);
SPAN_S_VAR(byte, extra_info, obuf);
extra_info = obuf.subref(
"bad extra_info offset %#x"
, skip, take);
// byte * const eistart = raw_bytes(extra_info, 0);
memcpy
(&oh, extra_info, take);
extra_info += take;
skip += take;
unsigned objs = oh.objects;
if
((
int
) objs <= 0 || (iobjs > 2 && isection[2].size == 0))
throwCantUnpack(
"unexpected value in the PE header"
);
Array(pe_section_t, osection, objs);
take =
sizeof
(pe_section_t) * objs;
extra_info = obuf.subref(
"bad extra section size at %#x"
, skip, take);
memcpy
(osection, extra_info, take);
extra_info += take;
skip += take;
rvamin = osection[0].vaddr;
if
(iobjs > 2) {
// read the noncompressed section
ibuf.dealloc();
ibuf.alloc(isection[2].size);
fi->seek(isection[2].rawdataptr, SEEK_SET);
fi->readx(ibuf, ibufgood = isection[2].size);
}
// unfilter
if
(ph.filter) {
Filter ft(ph.level);
ft.init(ph.filter, oh.codebase - rvamin);
ft.cto = (byte) ph.filter_cto;
OCHECK(obuf + (oh.codebase - rvamin), oh.codesize);
ft.unfilter(obuf + (oh.codebase - rvamin), oh.codesize);
}
// FIXME: ih.flags is checked here because of a bug in UPX 0.92
if
(ih.flags & IMAGE_FILE_RELOCS_STRIPPED) {
oh.flags |= IMAGE_FILE_RELOCS_STRIPPED;
ODADDR(PEDIR_RELOC) = 0;
ODSIZE(PEDIR_RELOC) = 0;
}
rebuildImports<LEXX>(extra_info, ord_mask, set_oft);
rebuildRelocs(extra_info,
sizeof
(ih.imagebase) * 8, oh.flags, oh.imagebase);
rebuildTls();
rebuildExports();
if
(iobjs > 3) {
// read the resource section if present
ibuf.dealloc();
ibuf.alloc(isection[3].size);
fi->seek(isection[3].rawdataptr, SEEK_SET);
fi->readx(ibuf, ibufgood = isection[3].size);
}
rebuildResources(extra_info, isection[ih.objects - 1].vaddr);
// FIXME: this does bad things if the relocation section got removed
// during compression ...
// memset(eistart, 0, ptr_udiff_bytes(extra_info, eistart) + 4);
// fill the data directory
ODADDR(PEDIR_DEBUG) = 0;
ODSIZE(PEDIR_DEBUG) = 0;
ODADDR(PEDIR_IAT) = 0;
ODSIZE(PEDIR_IAT) = 0;
ODADDR(PEDIR_BOUND_IMPORT) = 0;
ODSIZE(PEDIR_BOUND_IMPORT) = 0;
setOhHeaderSize(osection);
oh.chksum = 0;
// write decompressed file
if
(fo) {
unsigned ic = 0;
while
(ic < objs && osection[ic].rawdataptr == 0)
ic++;
ibuf.dealloc();
ibuf.alloc(osection[ic].rawdataptr);
ibuf.clear();
infoHeader(
"[Writing uncompressed file]"
);
// write header + decompressed file
fo->write(&oh,
sizeof
(oh));
fo->write(osection, objs *
sizeof
(pe_section_t));
fo->write(ibuf, osection[ic].rawdataptr - fo->getBytesWritten());
for
(ic = 0; ic < objs; ic++)
if
(osection[ic].rawdataptr)
fo->write(obuf + (osection[ic].vaddr - rvamin),
ALIGN_UP(osection[ic].size, oh.filealign));
copyOverlay(fo, overlay, obuf);
}
ibuf.dealloc();
}
|
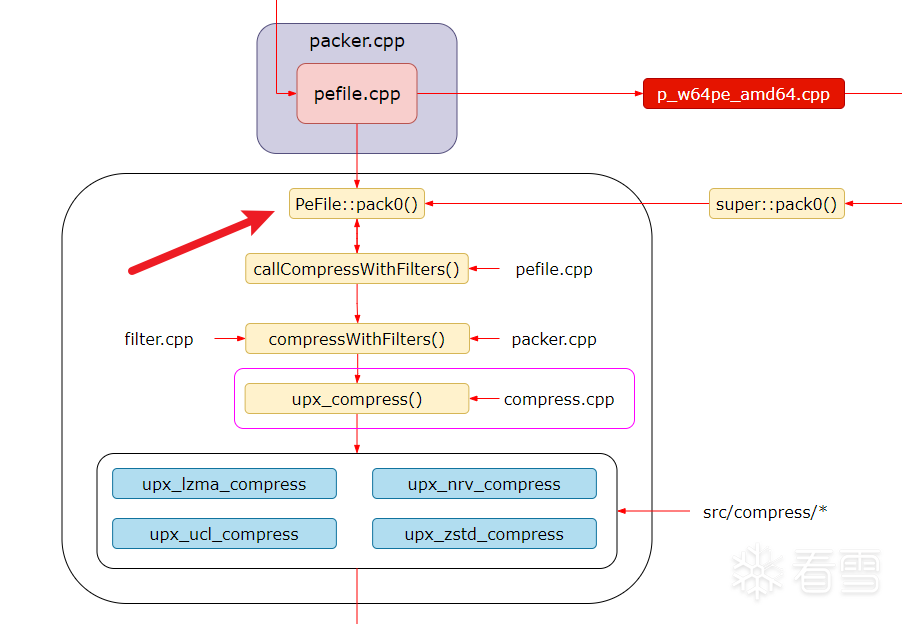
PeFile::pack0 执行步骤总结如下:
- 读取并解析 PE 文件的相关信息,如头部数据,区段信息等。
- 将 PE 文件的代码和数据进行压缩,通常会使用某种压缩算法。
- 生成一段解压缩的代码并添加到压缩后的 PE 文件中,以便在运行时解压缩并执行原始的代码。
- 预检查:在函数的开头部分,进行了一些预检查。包括检查 PE 文件的一些属性,例如是否需要完整性检查等。对应的代码在函数的开头部分,例如:
|
1
2
|
if
(opt->exact)
throwCantPackExact();
|
这一段代码检查了是否需要精确打包。如果需要,则抛出异常。
- 处理PE文件的各个部分:在函数的中间部分,处理了PE文件的各个部分,包括导入表,资源,TLS(线程局部存储),重定位等等。对应的代码在函数的中间部分,例如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
const
unsigned dllstrings = processImports();
processTls(&tlsiv);
// call before processRelocs!!
processLoadConf(&loadconfiv);
processResources(&res);
processExports(&xport);
processRelocs();
|
这一段代码处理了 PE 文件的导入表,TLS,加载配置,资源,导出表和重定位。
- 对文件进行打包和压缩:在处理完所有的部分后,开始对文件进行打包和压缩。在这个过程中,可能会对文件进行一些修改,例如修改PE头部,添加或删除某些段等。对应的代码在函数的后半部分,例如:
|
1
|
callCompressWithFilters(ft, filter_strategy, ih.codebase);
|
这一段代码调用了一个函数来进行压缩,并使用了过滤器。
- 将处理后的数据写入到输出文件,并复制覆盖层:最后,将处理后的数据写入到输出文件,并复制文件的覆盖层(如果存在的话)。对应的代码在函数的最后部分,例如:
|
1
2
3
4
|
fo->write(&oh,
sizeof
(oh));
fo->write(osection,
sizeof
(osection[0]) * oobjs);
...
copyOverlay(fo, overlay, obuf);
|
这一段代码将处理后的 PE 头部和各个部分写入到输出文件,然后复制文件的覆盖层。 复制覆盖层是指在原始的可执行文件压缩过程中,一些数据并没有被压缩,这部分数据通常被称为覆盖层(overlay)。这可能包括一些附加的未压缩数据,**例如数字签名,不会被压缩。**在解压缩过程中,这部分覆盖层数据需要被直接复制到解压缩的文件中,而不需要进行解压缩处理。
p_w64pe_amd64.cpp
接下来是 p_w64pe_amd64.cpp,p_w64pe_amd64.cpp 实现了针对64位PE文件的压缩打包逻辑,而 pefile.cpp 包含了PE文件格式的通用处理逻辑。p_w64pe_amd64.cpp是对pefile.cpp模板的复用:
- p_w64pe_amd64.cpp 继承自 Packer 和 PeFile 类,具体实现了64位PE文件的压缩打包操作,p_w64pe_amd64.cpp中的pack0()方法是PackW64PeAmd64类中的成员方法,它调用了父类PeFile的pack0()模板方法进行压缩。
- PeFile 类在 pefile.cpp 中实现,它包含了针对PE文件格式的通用处理逻辑,如读取PE头信息、导入表处理、重定位表处理等。
- p_w64pe_amd64.cpp 重用了PeFile类的功能,并实现了64位PE特有的压缩打包逻辑。
- 在 p_w64pe_amd64.cpp 中,关键的pack()方法会调用PeFile::pack0()进行实际的压缩工作。
- PeFile::pack0() 实现了压缩的通用流程,读取原始文件信息、压缩主代码段、生成新头信息等。
- 所以 p_w64pe_amd64.cpp 依赖并复用了 pefile.cpp 中PeFile类的通用功能,并在此基础上实现64位PE文件的特定处理。
对于64位PE,p_w64pe_amd64.cpp中的pack0()会实例化PeFile::pack0<LE64>(),而PeFile32和PeFile64则分别实例化PeFile::pack0<LE32>()和PeFile::pack0<LE64>()
接着分析p_w64pe_amd64.cpp的源码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
|
/
*
p_w64pe_amd64.cpp
-
-
This
file
is
part of the UPX executable compressor.
*
/
#include "conf.h"
#include "file.h"
#include "filter.h"
#include "packer.h"
#include "pefile.h"
#include "p_w64pe_amd64.h"
#include "linker.h"
static const CLANG_FORMAT_DUMMY_STATEMENT
#include "stub/amd64-win64.pe.h"
/
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
/
/
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
/
PackW64PeAmd64::PackW64PeAmd64(InputFile
*
f) :
super
(f) { use_stub_relocs
=
false; }
PackW64PeAmd64::~PackW64PeAmd64() noexcept {}
const
int
*
PackW64PeAmd64::getCompressionMethods(
int
method,
int
level) const {
bool
small
=
ih.codesize
+
ih.datasize <
=
256
*
1024
;
return
Packer::getDefaultCompressionMethods_le32(method, level, small);
}
const
int
*
PackW64PeAmd64::getFilters() const {
static const
int
filters[]
=
{
0x49
, FT_END};
return
filters;
}
Linker
*
PackW64PeAmd64::newLinker() const {
return
new ElfLinkerAMD64; }
/
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
/
/
pack
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
/
bool
PackW64PeAmd64::canPack() {
if
(!readFileHeader())
return
false;
checkMachine(ih.cpu);
if
(ih.cpu !
=
IMAGE_FILE_MACHINE_AMD64)
return
false;
return
true;
}
void PackW64PeAmd64::buildLoader(const
Filter
*
ft) {
/
/
recompute tlsindex (see pack() below)
unsigned tmp_tlsindex
=
tlsindex;
const unsigned oam1
=
ih.objectalign
-
1
;
const unsigned newvsize
=
(ph.u_len
+
rvamin
+
ph.overlap_overhead
+
oam1) & ~oam1;
if
(tlsindex && ((newvsize
-
ph.c_len
-
1024
+
oam1) & ~oam1) > tlsindex
+
4
)
tmp_tlsindex
=
0
;
/
/
prepare loader
initLoader(stub_amd64_win64_pe, sizeof(stub_amd64_win64_pe),
2
);
addLoader(
"START"
);
if
(ih.entry && isdll)
addLoader(
"PEISDLL0"
);
if
(isefi)
addLoader(
"PEISEFI0"
);
addLoader(isdll ?
"PEISDLL1"
: "
", "
PEMAIN01",
icondir_count >
1
? (icondir_count
=
=
2
?
"PEICONS1"
:
"PEICONS2"
) : "",
tmp_tlsindex ?
"PETLSHAK"
: "
", "
PEMAIN02",
/
/
ph.first_offset_found
=
=
1
?
"PEMAIN03"
: "",
M_IS_LZMA(ph.method) ?
"LZMA_HEAD,LZMA_ELF00,LZMA_DEC20,LZMA_TAIL"
: M_IS_NRV2B(ph.method) ?
"NRV_HEAD,NRV2B"
: M_IS_NRV2D(ph.method) ?
"NRV_HEAD,NRV2D"
: M_IS_NRV2E(ph.method) ?
"NRV_HEAD,NRV2E"
:
"UNKNOWN_COMPRESSION_METHOD"
,
/
/
getDecompressorSections(),
/
*
multipass ?
"PEMULTIP"
:
*
/
"
", "
PEMAIN10");
addLoader(tmp_tlsindex ?
"PETLSHAK2"
: "");
if
(ft
-
>
id
) {
const unsigned texv
=
ih.codebase
-
rvamin;
assert
(ft
-
>calls >
0
);
addLoader(texv ?
"PECTTPOS"
:
"PECTTNUL"
);
addLoader(
"PEFILTER49"
);
}
if
(soimport)
addLoader(
"PEIMPORT"
, importbyordinal ?
"PEIBYORD"
: "
", kernel32ordinal ? "
PEK32ORD
" : "
",
importbyordinal ?
"PEIMORD1"
: "
", "
PEIMPOR2
", isdll ? "
PEIERDLL
" : "
PEIEREXE",
"PEIMDONE"
);
if
(sorelocs) {
addLoader(soimport
=
=
0
|| soimport
+
cimports !
=
crelocs ?
"PERELOC1"
:
"PERELOC2"
,
"PERELOC3"
, big_relocs ?
"REL64BIG"
: "
", "
RELOC64J");
if
(
0
) {
addLoader(big_relocs &
6
?
"PERLOHI0"
: "
", big_relocs & 4 ? "
PERELLO0
" : "
",
big_relocs &
2
?
"PERELHI0"
: "");
}
}
if
(use_dep_hack)
addLoader(
"PEDEPHAK"
);
/
/
NEW: TLS callback support PART
1
, the callback handler installation
-
Stefan Widmann
if
(use_tls_callbacks)
addLoader(
"PETLSC"
);
addLoader(
"PEMAIN20"
);
if
(use_clear_dirty_stack)
addLoader(
"CLEARSTACK"
);
addLoader(
"PEMAIN21"
);
if
(ih.entry && isdll)
addLoader(
"PEISDLL9"
);
if
(isefi)
addLoader(
"PEISEFI9"
);
addLoader(ih.entry || !ilinker ?
"PEDOJUMP"
:
"PERETURN"
);
/
/
NEW: TLS callback support PART
2
, the callback handler
-
Stefan Widmann
if
(use_tls_callbacks)
addLoader(
"PETLSC2"
);
addLoader(
"IDENTSTR,UPX1HEAD"
);
}
bool
PackW64PeAmd64::needForceOption() const {
/
/
return
true
if
we need `
-
-
force` to pack this
file
bool
r
=
false;
r |
=
(ih.opthdrsize !
=
0xf0
);
/
/
optional header size
is
0xF0
in
PE32
+
files
r |
=
((ih.flags & IMAGE_FILE_EXECUTABLE_IMAGE)
=
=
0
);
r |
=
((ih.flags & IMAGE_FILE_32BIT_MACHINE) !
=
0
);
/
/
32
bit machine flag may
not
be
set
r |
=
(ih.coffmagic !
=
0x20b
);
/
/
COFF magic
is
0x20B
in
PE32
+
files
r |
=
(ih.entry
=
=
0
&& !isdll);
r |
=
(ih.ddirsentries !
=
16
);
return
r;
}
void PackW64PeAmd64::defineSymbols(unsigned ncsection, unsigned upxsection, unsigned sizeof_oh,
unsigned ic, unsigned s1addr) {
const unsigned myimport
=
ncsection
+
soresources
-
rvamin;
/
/
patch loader
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"original_entry"
, ih.entry);
if
(use_dep_hack) {
/
/
This works around a
"protection"
introduced
in
MSVCRT80, which
/
/
works like this:
/
/
When the compiler detects that it would link
in
some code
from
its
/
/
C runtime library which references some data
in
a read only
/
/
section then it compiles
in
a runtime check whether that data
is
/
/
still
in
a read only section by looking at the pe header of the
/
/
file
. If this check fails the runtime does
"interesting"
things
/
/
like
not
running the floating point initialization code
-
the result
/
/
is
a R6002 runtime error.
/
/
These supposed to be read only addresses are covered by the sections
/
/
UPX0 & UPX1
in
the compressed files, so we have to patch the PE header
/
/
in
the memory. And the page on which the PE header
is
stored
is
read
/
/
only so we must make it rw, fix the flags (i.e. clear
/
/
IMAGE_SCN_MEM_WRITE of osection[x].flags),
and
make it ro again.
/
/
rva of the most significant byte of member
"flags"
in
section
"UPX0"
const unsigned swri
=
pe_offset
+
sizeof_oh
+
sizeof(pe_section_t)
-
1
;
/
/
make sure we only touch the minimum number of pages
const unsigned addr
=
0u
-
rvamin
+
swri;
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"swri"
, addr &
0xfff
);
/
/
page offset
/
/
check whether osection[
0
].flags
and
osection[
1
].flags
/
/
are on the same page
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"vp_size"
, ((addr &
0xfff
)
+
0x28
>
=
0x1000
) ?
0x2000
:
0x1000
);
/
/
2
pages
or
1
page
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"vp_base"
, addr & ~
0xfff
);
/
/
page mask
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"VirtualProtect"
, ilinkerGetAddress(
"kernel32.dll"
,
"VirtualProtect"
));
}
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"start_of_relocs"
, crelocs);
if
(ilinker) {
if
(!isdll)
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"ExitProcess"
, ilinkerGetAddress(
"kernel32.dll"
,
"ExitProcess"
));
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"GetProcAddress"
, ilinkerGetAddress(
"kernel32.dll"
,
"GetProcAddress"
));
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"kernel32_ordinals"
, myimport);
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"LoadLibraryA"
, ilinkerGetAddress(
"kernel32.dll"
,
"LoadLibraryA"
));
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"start_of_imports"
, myimport);
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"compressed_imports"
, cimports);
}
if
(M_IS_LZMA(ph.method)) {
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"lzma_c_len"
, ph.c_len
-
2
);
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"lzma_u_len"
, ph.u_len);
}
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"filter_buffer_start"
, ih.codebase
-
rvamin);
/
/
in
case of overlapping decompression, this hack
is
needed,
/
/
because windoze zeroes the word pointed by tlsindex before
/
/
it starts programs
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"tls_value"
,
(tlsindex
+
4
> s1addr) ? get_le32(obuf
+
tlsindex
-
s1addr
-
ic) :
0
);
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"tls_address"
, tlsindex
-
rvamin);
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"icon_delta"
, icondir_count
-
1
);
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"icon_offset"
, ncsection
+
icondir_offset
-
rvamin);
const unsigned esi0
=
s1addr
+
ic;
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"start_of_uncompressed"
,
0u
-
esi0
+
rvamin);
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"start_of_compressed"
, esi0);
if
(use_tls_callbacks) {
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"tls_callbacks_ptr"
, tlscb_ptr
-
ih.imagebase);
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"tls_module_base"
,
0u
-
rvamin);
}
linker
-
>defineSymbol(
"START"
, upxsection);
}
void PackW64PeAmd64::setOhHeaderSize(const pe_section_t
*
osection) {
/
/
SizeOfHeaders
oh.headersize
=
ALIGN_UP(pe_offset
+
sizeof(oh)
+
sizeof(
*
osection)
*
oh.objects, oh.filealign);
}
void PackW64PeAmd64::pack(OutputFile
*
fo) {
unsigned mask
=
(
1u
<< IMAGE_SUBSYSTEM_WINDOWS_GUI) | (
1u
<< IMAGE_SUBSYSTEM_WINDOWS_CUI) |
(
1u
<< IMAGE_SUBSYSTEM_EFI_APPLICATION) |
(
1u
<< IMAGE_SUBSYSTEM_EFI_BOOT_SERVICE_DRIVER) |
(
1u
<< IMAGE_SUBSYSTEM_EFI_RUNTIME_DRIVER) | (
1u
<< IMAGE_SUBSYSTEM_EFI_ROM);
super
::pack0(fo, mask,
0x0000000140000000ULL
);
}
/
*
vim:
set
ts
=
4
sw
=
4
et:
*
/
|
在给定的源代码中,定义了类的构造函数、析构函数、成员函数,这些函数的功能为:
PackW64PeAmd64(InputFile *f): 这是类的构造函数,它接受一个指向InputFile类型对象的指针f,这个对象可能是用来表示待压缩的输入文件。~PackW64PeAmd64() noexcept: 这是类的析构函数,它在类的对象不再需要时被调用,用于做一些清理工作。getCompressionMethods(int method, int level) const: 这个函数返回一个指向整型数组的指针,这个数组表示可用于压缩的方法,参数method和level可能用于指定或调整压缩方法和级别。getFilters() const: 这个函数返回一个指向整型数组的指针,这个数组表示用于压缩前后处理的过滤器。newLinker() const: 这个函数返回一个指向Linker类型对象的指针,这个对象可能用于处理文件的链接问题。canPack(): 这个函数检查当前的输入文件是否可以被压缩,返回一个布尔值。buildLoader(const Filter *ft): 这个函数用于构建加载器,它接受一个指向Filter类型对象的指针ft,这个对象可能用于指定过滤器。needForceOption() const: 这个函数检查是否需要强制压缩选项,返回一个布尔值。defineSymbols(unsigned ncsection, unsigned upxsection, unsigned sizeof_oh, unsigned ic, unsigned zzzzzzzzzzs1addr): 这个函数用于定义链接器的符号。setOhHeaderSize(const pe_section_t *osection): 这个函数用于设置可选头部的大小。pack(OutputFile *fo): 这个函数用于压缩文件,它接受一个指向OutputFile类型对象的指针fo,这个对象可能是用来表示压缩后的输出文件。
主要打包函数在PackW64PeAmd64::pack(OutputFile *fo) :
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
void PackW64PeAmd64::pack(OutputFile
*
fo) {
unsigned mask
=
(
1u
<< IMAGE_SUBSYSTEM_WINDOWS_GUI) | (
1u
<< IMAGE_SUBSYSTEM_WINDOWS_CUI) |
(
1u
<< IMAGE_SUBSYSTEM_EFI_APPLICATION) |
(
1u
<< IMAGE_SUBSYSTEM_EFI_BOOT_SERVICE_DRIVER) |
(
1u
<< IMAGE_SUBSYSTEM_EFI_RUNTIME_DRIVER) | (
1u
<< IMAGE_SUBSYSTEM_EFI_ROM);
super
::pack0(fo, mask,
0x0000000140000000ULL
);
}
|
super是访问父类成员的关键字,super::pack0调用了父类PeFile的pack0()模板方法进行实际的压缩工作,所以从这里开始正式执行pefile.cpp模板提供的打包函数PeFile::pack0()。
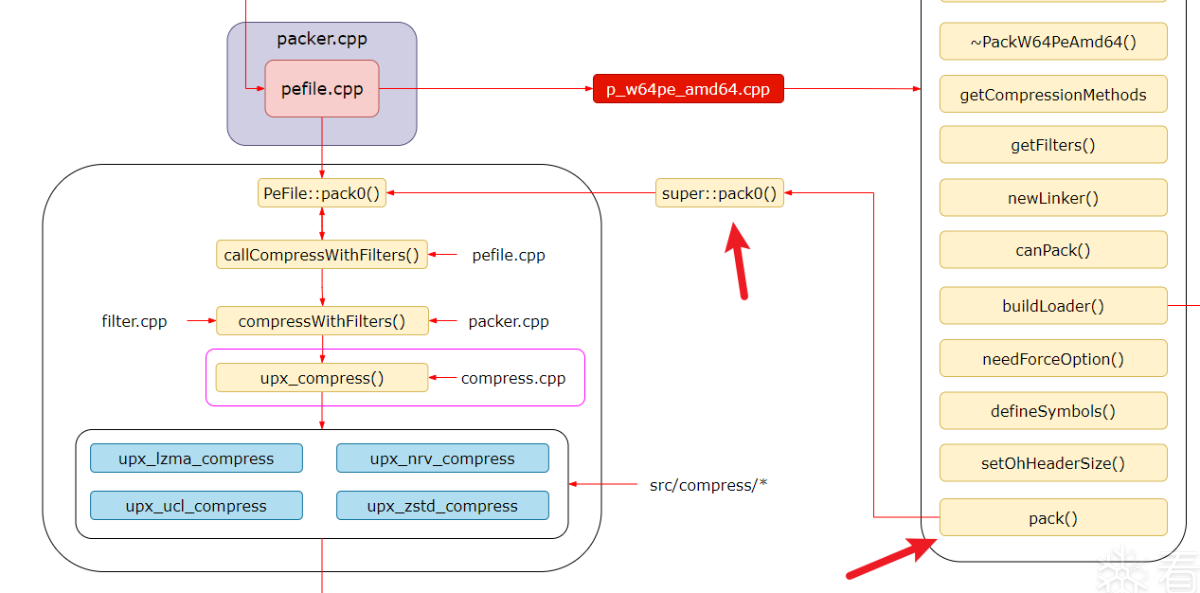
filter.cpp
filter是 UPX 中用于预处理输入文件的数据流的组件,压缩的程序需要经过过滤器filter处理数据流来便于压缩,它可以实现一些转换,从而改善输入数据的压缩效果。filter的核心思想是转换相对跳转和调用转为绝对地址,以便更好地压缩。
filter.h中公有类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
|
/*************************************************************************
// A filter is a reversible operation that modifies a given
// block of memory.
//
// A filter can fail and return false. In this case the buffer
// must be unmodified (or otherwise restored).
//
// If a filter fails and somehow cannot restore the block it must
// call throwFilterException() - this will cause the compression
// to fail.
//
// Unfilters throw exceptions in case of errors.
//
// The main idea behind filters is to convert relative jumps and calls
// to absolute addresses so that the buffer compresses better.
**************************************************************************/
class
Filter final {
public
:
explicit
Filter(
int
level) noexcept;
void
init(
int
id = 0, unsigned addvalue = 0) noexcept;
bool
filter(SPAN_0(byte) buf, unsigned buf_len);
void
unfilter(SPAN_0(byte) buf, unsigned buf_len,
bool
verify_checksum =
false
);
void
verifyUnfilter();
bool
scan(SPAN_0(
const
byte) buf, unsigned buf_len);
static
bool
isValidFilter(
int
filter_id);
static
bool
isValidFilter(
int
filter_id,
const
int
*allowed_filters);
public
:
// Will be set by each call to filter()/unfilter().
// Read-only afterwards.
byte *buf = nullptr;
unsigned buf_len = 0;
// Checksum of the buffer before applying the filter
// or after un-applying the filter.
unsigned adler;
// Input parameters used by various filters.
unsigned addvalue;
const
int
*preferred_ctos = nullptr;
// Input/output parameters used by various filters
byte cto;
// call trick offset
// Output used by various filters. Read only.
unsigned calls;
unsigned noncalls;
unsigned wrongcalls;
unsigned firstcall;
unsigned lastcall;
unsigned n_mru;
// ctojr only
// Read only.
int
id;
private
:
int
clevel;
// compression level
};
|
根据源码可以总结出过滤器运行流程大致为:initFilter->isValidFilter -> getFilter -> do_filter
初始化filter -> 判断filter是否有效 -> 获取filter的过滤器ID对应的FilterEntry对象 -> 根据方法进行填充
在filter.h中可以看到FilterEntry结构体的定义:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
struct
FilterEntry {
int
id;
// 0 .. 255
unsigned min_buf_len;
unsigned max_buf_len;
int
(*do_filter)(Filter *);
// filter a buffer
int
(*do_unfilter)(Filter *);
// unfilter a buffer
int
(*do_scan)(Filter *);
// scan a buffer
};
|
do_filter 和 do_unfilter 是函数指针,它们指向实现过滤和解过滤操作的函数。举个例子来理解filter:
如果过滤器ID是0x01(Fill holes),那么在压缩阶段,filter() 函数将会调用 do_filter() 函数,该函数会用某个字节(如0x00或0xFF)填充输入数据流中的空洞。在解压缩阶段,unfilter()函数将会调用do_unfilter()函数,该函数会从数据流中移除这些填充字节,恢复原始的数据流。
过滤器的种类和功能包括:(0x00代表过滤器ID)
Page align(0x00):将输入流对齐到页面边界,通常为 4096 字节。Fill holes(0x01):用某个字节(如 0x00 或 0xff)填充输入流中的空洞。Fix references(0x02):修复输入流中的内部引用。Remove duplicates(0x03):删除输入流中的重复字节序列。Data swap(0x04):交换输入数据的字节序。UPX1 fix(0x10):修复 UPX v1 打包格式中的引用。Delta encoding(0x11):差分编码,将输入数据表示为原始数据与初始数据之间的差异。MRU encoding(0x12):最近最先使用编码,使用可能重复的数字来表示输入流中的值。
过滤器通过上面的方式能够预处理输入流从而给予压缩算法更好的输入,它位于 UPX 的 Packer 组件之前执行,Packer 默认会尝试使用不同的过滤器并选择压缩效果最好的那个。如果想使用 Remove duplicates,通过命令行参数 --filter 可以指定, 我测试的时候貌似没什么效果。
|
1
|
upx
-
-
filter
=
0x03
myprogram.exe
|
compress.cpp*
在src/compress/compress.cpp文件中,定义了三个函数:upx_compress、upx_decompress、upx_test_overlap,分别用来压缩、解压缩、测试解压缩过程中是否有数据覆盖。upx_compress函数是一个通用的接口,用于根据指定的压缩方法对数据进行压缩。具体的压缩方法包括:LZMA,NRV,UCL,ZSTD等。你可以在以下代码中看到这个函数:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
int
upx_decompress(
const
upx_bytep src, unsigned src_len, upx_bytep dst, unsigned *dst_len,
int
method,
const
upx_compress_result_t *cresult) {
int
r = UPX_E_ERROR;
assert
(*dst_len > 0);
assert
(src_len < *dst_len);
// must be compressed
if
(cresult && cresult->debug.method == 0)
cresult = nullptr;
if
(__acc_cte(
false
)) {
}
#if (WITH_LZMA)
else
if
(M_IS_LZMA(method))
r = upx_lzma_decompress(src, src_len, dst, dst_len, method, cresult);
#endif
#if (WITH_NRV)
else
if
((M_IS_NRV2B(method) || M_IS_NRV2D(method) || M_IS_NRV2E(method)) && !opt->prefer_ucl)
r = upx_nrv_decompress(src, src_len, dst, dst_len, method, cresult);
#endif
#if (WITH_UCL)
else
if
(M_IS_NRV2B(method) || M_IS_NRV2D(method) || M_IS_NRV2E(method))
r = upx_ucl_decompress(src, src_len, dst, dst_len, method, cresult);
#endif
#if (WITH_ZLIB)
else
if
(M_IS_DEFLATE(method))
r = upx_zlib_decompress(src, src_len, dst, dst_len, method, cresult);
#endif
#if (WITH_ZSTD)
else
if
(M_IS_ZSTD(method))
r = upx_zstd_decompress(src, src_len, dst, dst_len, method, cresult);
#endif
else
{
throwInternalError(
"unknown decompression method"
);
}
return
r;
}
|
根据指定的压缩方法,upx_compress函数将调用对应的压缩函数:
- LZMA压缩:如果压缩方法是LZMA,那么会调用
upx_lzma_compress函数。LZMA(Lempel-Ziv-Markov chain Algorithm)是一种非常有效的压缩算法,它可以提供非常高的压缩比。
|
1
2
|
else
if
(M_IS_LZMA(method))
r = upx_lzma_compress(src, src_len, dst, dst_len, cb, method, level, cconf, cresult);
|
- NRV压缩:如果压缩方法是NRV,那么会调用
upx_nrv_compress函数。NRV是UCL压缩库中的一种压缩算法。
|
1
2
|
else
if
((M_IS_NRV2B(method) || M_IS_NRV2D(method) || M_IS_NRV2E(method)) && !opt->prefer_ucl)
r = upx_nrv_compress(src, src_len, dst, dst_len, cb, method, level, cconf, cresult);
|
- UCL压缩:如果压缩方法是UCL,那么会调用
upx_ucl_compress函数。
|
1
2
|
else
if
(M_IS_NRV2B(method) || M_IS_NRV2D(method) || M_IS_NRV2E(method))
r = upx_ucl_compress(src, src_len, dst, dst_len, cb, method, level, cconf, cresult);
|
- ZSTD压缩:如果压缩方法是ZSTD,那么会调用
upx_zstd_compress函数。ZSTD是由Facebook开发的一种快速实时压缩算法。
|
1
2
|
else
if
(M_IS_ZSTD(method))
r = upx_zstd_compress(src, src_len, dst, dst_len, cb, method, level, cconf, cresult);
|
以上代码中的upx_lzma_compress,upx_nrv_compress,upx_ucl_compress,upx_zstd_compress等函数是具体的压缩函数的调用,它们的具体实现在src/compress/*文件夹中。
upx_decompress与upx_compress相对应,执行的是与之相反的功能。upx_test_overlap函数被用来测试在解压缩过程中是否有数据覆盖的发生。数据覆盖是指解压缩的输出会覆盖未解压缩的输入数据,这通常在解压缩的输出和输入共享相同的内存区域并且输出比输入大时发生,这种情况在解压缩过程中是需要避免的。
在UPX中这种情况可能发生,因为UPX的设计目标是使得解压缩可以在原地进行,即解压缩的输出可以覆盖压缩的输入,以节省内存。但是,如果解压缩的输出数据比输入数据大,并且输出和输入的内存区域有重叠,那么就会发生数据覆盖。为了避免这种情况,UPX在解压缩之前会使用upx_test_overlap函数来测试是否会发生数据覆盖。
upx_test_overlap函数接受压缩数据和解压缩数据的内存区域,以及预期的解压缩数据的大小等参数。然后,它会调用相应的*_test_overlap函数(例如upx_lzma_test_overlap、upx_ucl_test_overlap等),来测试给定的解压缩方法是否会导致数据覆盖。如果测试发现会发生数据覆盖,那么upx_test_overlap函数会返回一个错误代码。否则,它会返回一个表示成功的代码。
compress algorithm
关于upx压缩算法部分,在src/compress目录下,upx 主要使用了下面几种压缩算法:
- LZMA 是 Lempel–Ziv–Markov chain 算法,它属于字典编码类压缩算法,压缩率较高。
- UCL 是Universal Codec Library,也是一个字典编码类算法。
- Zlib 是 DEFLATE算法的实现,也属于字典编码类压缩算法。
- Zstandard(Zstd) 是 Facebook开发的压缩算法,它采用哈希函数的技术加快搜索过程。
这四种算法各有优劣:
- LZMA 和 UCL 压缩率较高,但速度相对慢一些。适合打包桌面软件使用。
- Zlib 和 Zstd 压缩率在中等水平,但速度快,适合网络传输。
在代码中,upx 对算法进行打包,根据 method 参数的不同,选择调用相应压缩算法的实现,例如在src/compress/compress.cpp:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
if
(M_IS_LZMA(method)) {
r = upx_lzma_compress(...);
// 使用LZMA算法
}
else
if
(M_IS_ZSTD(method)) {
r = upx_zstd_compress(...);
// 使用Zstd算法
}
|
什么是字典编码类压缩算法?字典编码类压缩算法是一类基于重复字符串匹配的压缩算法,它的主要思想是:
- 构建一个字符串到编码的映射(字典)
- 在要压缩的数据流中查找重复的字符串
- 将重复的字符串替换为字典中的编码
典型的字典编码类压缩算法有:LZ77、LZ78、LZW、DEFLATE 等。具体的做法是:
- 先将光标停在要压缩的数据流的起点
- 查找一个没有在字典中出现过的字符串
- 将这个字符串添加到字典中并分配一个编码
- 将这个编码写到压缩的数据流中
- 光标后移到该字符串结束点
- 重复上述过程直到压缩完所有数据
这样可以实现压缩的效果:
- 原始字符串 ==> 较短的编码字符串
在这篇文章算法部分不详细展开,后续可能会进行进一步分析。
Loader
p_w64pe_amd64.cpp: buildLoader
这里我们要回到p_w64pe_amd64.cpp的源码中进行分析,下面是p_w64pe_amd64中PackW64PeAmd64成员函数buildLoader:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
|
void
PackW64PeAmd64::buildLoader(
const
Filter *ft) {
// recompute tlsindex (see pack() below)
unsigned tmp_tlsindex = tlsindex;
const
unsigned oam1 = ih.objectalign - 1;
const
unsigned newvsize = (ph.u_len + rvamin + ph.overlap_overhead + oam1) & ~oam1;
if
(tlsindex && ((newvsize - ph.c_len - 1024 + oam1) & ~oam1) > tlsindex + 4)
tmp_tlsindex = 0;
// prepare loader
initLoader(stub_amd64_win64_pe,
sizeof
(stub_amd64_win64_pe), 2);
addLoader(
"START"
);
if
(ih.entry && isdll)
addLoader(
"PEISDLL0"
);
if
(isefi)
addLoader(
"PEISEFI0"
);
addLoader(isdll ?
"PEISDLL1"
:
""
,
"PEMAIN01"
,
icondir_count > 1 ? (icondir_count == 2 ?
"PEICONS1"
:
"PEICONS2"
) :
""
,
tmp_tlsindex ?
"PETLSHAK"
:
""
,
"PEMAIN02"
,
// ph.first_offset_found == 1 ? "PEMAIN03" : "",
M_IS_LZMA(ph.method) ?
"LZMA_HEAD,LZMA_ELF00,LZMA_DEC20,LZMA_TAIL"
: M_IS_NRV2B(ph.method) ?
"NRV_HEAD,NRV2B"
: M_IS_NRV2D(ph.method) ?
"NRV_HEAD,NRV2D"
: M_IS_NRV2E(ph.method) ?
"NRV_HEAD,NRV2E"
:
"UNKNOWN_COMPRESSION_METHOD"
,
// getDecompressorSections(),
/*multipass ? "PEMULTIP" : */
""
,
"PEMAIN10"
);
addLoader(tmp_tlsindex ?
"PETLSHAK2"
:
""
);
if
(ft->id) {
const
unsigned texv = ih.codebase - rvamin;
assert
(ft->calls > 0);
addLoader(texv ?
"PECTTPOS"
:
"PECTTNUL"
);
addLoader(
"PEFILTER49"
);
}
if
(soimport)
addLoader(
"PEIMPORT"
, importbyordinal ?
"PEIBYORD"
:
""
, kernel32ordinal ?
"PEK32ORD"
:
""
,
importbyordinal ?
"PEIMORD1"
:
""
,
"PEIMPOR2"
, isdll ?
"PEIERDLL"
:
"PEIEREXE"
,
"PEIMDONE"
);
if
(sorelocs) {
addLoader(soimport == 0 || soimport + cimports != crelocs ?
"PERELOC1"
:
"PERELOC2"
,
"PERELOC3"
, big_relocs ?
"REL64BIG"
:
""
,
"RELOC64J"
);
if
(0) {
addLoader(big_relocs & 6 ?
"PERLOHI0"
:
""
, big_relocs & 4 ?
"PERELLO0"
:
""
,
big_relocs & 2 ?
"PERELHI0"
:
""
);
}
}
if
(use_dep_hack)
addLoader(
"PEDEPHAK"
);
// NEW: TLS callback support PART 1, the callback handler installation - Stefan Widmann
if
(use_tls_callbacks)
addLoader(
"PETLSC"
);
addLoader(
"PEMAIN20"
);
if
(use_clear_dirty_stack)
addLoader(
"CLEARSTACK"
);
addLoader(
"PEMAIN21"
);
if
(ih.entry && isdll)
addLoader(
"PEISDLL9"
);
if
(isefi)
addLoader(
"PEISEFI9"
);
addLoader(ih.entry || !ilinker ?
"PEDOJUMP"
:
"PERETURN"
);
// NEW: TLS callback support PART 2, the callback handler - Stefan Widmann
if
(use_tls_callbacks)
addLoader(
"PETLSC2"
);
addLoader(
"IDENTSTR,UPX1HEAD"
);
}
|
它的主要作用是创建和配置在解压缩UPX压缩文件时使用的加载器,buildLoader函数接受一个Filter类型的指针ft作为参数,这是表示在压缩和解压缩过程中使用的过滤器。buildLoader函数内主要使用了两个函数,都在packer.cpp中:
initLoader:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
void
Packer::initLoader(
const
void
*pdata,
int
plen,
int
small,
int
pextra) {
owner_delete(linker);
linker = newLinker();
assert
(bele == linker->bele);
linker->init(pdata, plen, pextra);
unsigned size;
char
const
*
const
ident = getIdentstr(&size, small);
linker->addSection(
"IDENTSTR"
, ident, size, 0);
}
|
addLoader:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
#define C const char *
#define N ACC_STATIC_CAST(void *, nullptr)
void
Packer::addLoader(C a) { addLoaderVA(a, N); }
void
Packer::addLoader(C a, C b) { addLoaderVA(a, b, N); }
void
Packer::addLoader(C a, C b, C c) { addLoaderVA(a, b, c, N); }
void
Packer::addLoader(C a, C b, C c, C d) { addLoaderVA(a, b, c, d, N); }
void
Packer::addLoader(C a, C b, C c, C d, C e) { addLoaderVA(a, b, c, d, e, N); }
void
Packer::addLoader(C a, C b, C c, C d, C e, C f) { addLoaderVA(a, b, c, d, e, f, N); }
void
Packer::addLoader(C a, C b, C c, C d, C e, C f, C g) { addLoaderVA(a, b, c, d, e, f, g, N); }
void
Packer::addLoader(C a, C b, C c, C d, C e, C f, C g, C h) {
addLoaderVA(a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, N);
}
void
Packer::addLoader(C a, C b, C c, C d, C e, C f, C g, C h, C i) {
addLoaderVA(a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, N);
}
void
Packer::addLoader(C a, C b, C c, C d, C e, C f, C g, C h, C i, C j) {
addLoaderVA(a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, N);
}
#undef C
#undef N
|
这段代码是对addLoader进行重载,addLoader为重载的函数,参数个数不同,用于接收不同个数的const char参数。#define C 和 #define N 是用定义宏来分别表示 const char 和 nullptr,每个addLoader内部都调用addLoaderVA,将可变参数打包传递给addLoaderVA,addLoaderVA才是实际的实现函数。
addLoaderVA:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
void
Packer::addLoaderVA(
const
char
*s, ...) {
va_list
ap;
va_start
(ap, s);
linker->addLoader(s, ap);
va_end
(ap);
}
|
addLoaderVA中使用了linker->addLoader(s, ap)将第一个固定参数 s 和可变参数 ap 传递给 linker 的 addLoader 方法,linker 是一个 ElfLinker类的对象,addLoader是ElfLinker类中定义的成员函数,inker->addLoader() 根据传入的第一个字符串参数和可变参数,将这些字符串添加到加载器中。
总结一下,buildLoader函数具体做了以下操作:
- 初始化加载器:
initLoader(stub_amd64_win64_pe, sizeof(stub_amd64_win64_pe), 2);用预定义的stub_amd64_win64_pe模板初始化加载器。 - 添加各种代码片段到加载器:
addLoader()函数用于向加载器添加不同的代码片段。这些代码片段由字符串参数标识,例如 "START","PEISDLL0","PEMAIN01"等,作为各个段的名称。 - 根据不同的条件添加对应的代码片段:例如,如果文件是DLL或EFI,或者使用了特定的压缩方法(如LZMA或NRV),那么将添加相应的代码片段。
- 支持TLS回调:如果启用了TLS回调(通过
use_tls_callbacks变量控制),则会添加支持TLS回调的代码片段。 - 最后,添加加载器的结束标记:"IDENTSTR,UPX1HEAD"。
标识符在amd64-win64.pe.S中:
linker.cpp*
根据源码我们可以发现 linker 是一个非常关键的类,主要用来构建和管理可执行文件的加载器。它的主要作用有:
- 管理加载器的各个Section。可以添加、查找Section。
- 提供加载器生成的框架。处理各个代码段的添加、重定位、链接,优化加载器的生成过程。
- 实现不同的重定位(Relocation)类型,针对不同架构做重定位处理。
- 维护符号(Symbol)信息。Symbol与Section相关联。
- 获取最终连接好的加载器。
- 封装可执行文件加载器的构建过程,如匹配算法、节对齐等。
- 链接可执行文件中的数据,使加载器可以访问。
- 提供便利的接口,如addLoader系列函数。
- 链接外部符号,能够获取导入表等信息。
对应函数进行分类来分析代码可知:
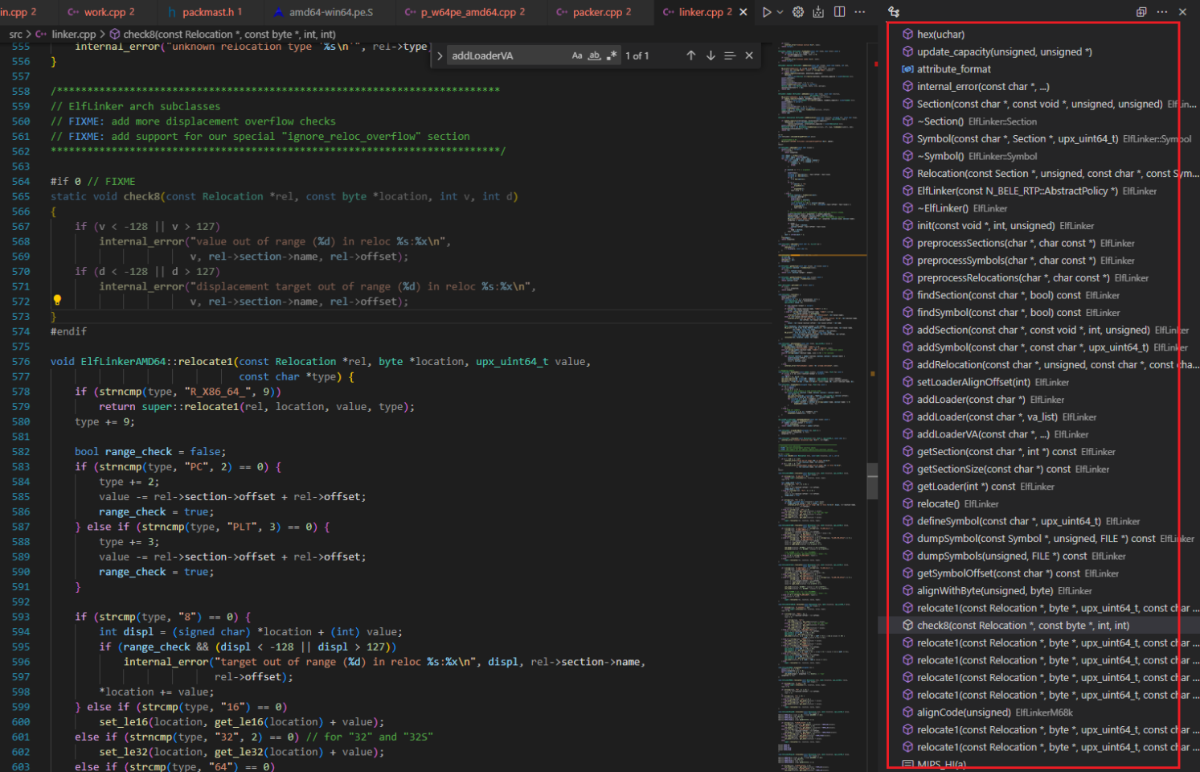
- 管理加载器的各个Section:
- addSection - 添加Section
- findSection - 查找Section
- getSection/getSectionSize - 获取Section信息
- 提供加载器生成的框架:
- init - 初始化加载器amd64-win64.pe.S
- addLoader - 添加加载器代码
- getLoader - 获取最终生成的加载器
- 实现不同的重定位(Relocation):
- relocate1 - 不同架构的重定位实现
- relocate - 进行重定位
- 维护符号信息:
- addSymbol - 添加符号
- defineSymbol - 定义符号
- getSymbolOffset - 获取符号偏移
- 获取最终连接好的加载器:
- getLoader - 获取最终的加载器代码
- 封装可执行文件加载器的构建过程:
- alignCode/alignData - 代码/数据对齐
- preprocess* - 预处理符号表和重定位信息
- 链接可执行文件中的数据:
- defineSymbol - 链接可执行文件符号
- 提供便利的接口:
- addLoader - 添加加载器代码段的接口
- 链接外部符号:
- defineSymbol - 可以链接外部库的符号
我们可以看到 p_w64pe_amd64.cpp 没有使用 getLoader() 函数,getLoader()是通用的加载器模板代码,而p_w64pe_amd64.cpp 针对具体的amd64 PE平台重写了buildLoader方法直接生成了amd64平台的加载器代码,因此只使用initLoader、addLoader就可以了。
amd64-win64.pe.S
在src/stub/src目录下可以看到这种名字为架构-系统.类型.S的汇编代码文件, 例如:amd64-win64.pe.S,这是针对windows 64位PE程序的汇编代码。
- amd64:指示该文件用于 AMD64(也称为 x86-64)架构
- win64:指示该文件用于 64 位 Windows 系统
- pe:指示该文件用于处理 PE(Portable Executable)
- .S:文件的扩展名,表明这是一个汇编语言源代码文件
这个汇编代码也整理的十分整齐,比如把入口点统一放在一起:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
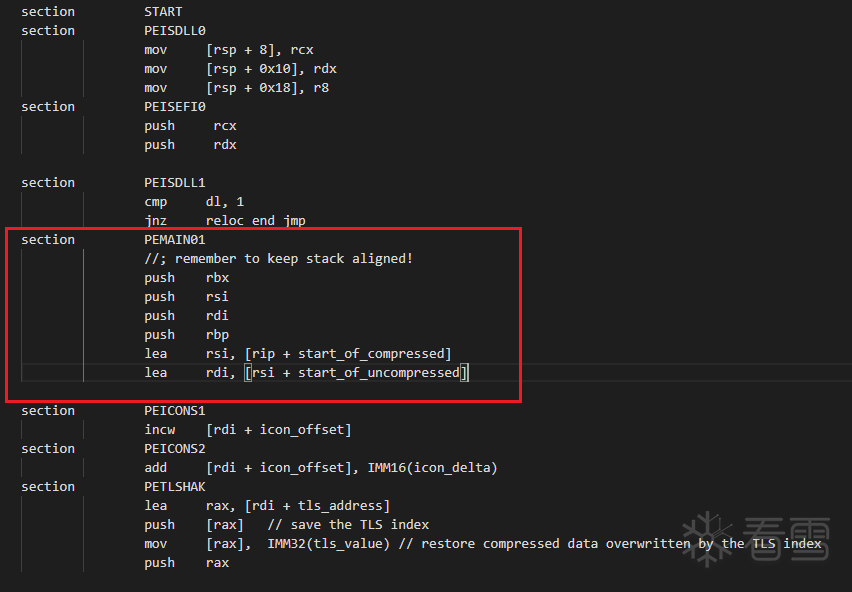
// =============
// ============= ENTRY POINT
// =============
section START
section PEISDLL0
mov [rsp + 8], rcx
mov [rsp + 0x10], rdx
mov [rsp + 0x18], r8
section PEISEFI0
push rcx
push rdx
section PEISDLL1
cmp dl, 1
jnz reloc_end_jmp
section PEMAIN01
//; remember to keep stack aligned!
push rbx
push rsi
push rdi
push rbp
lea rsi, [rip + start_of_compressed]
lea rdi, [rsi + start_of_uncompressed]
section PEICONS1
incw [rdi + icon_offset]
section PEICONS2
add [rdi + icon_offset], IMM16(icon_delta)
section PETLSHAK
lea rax, [rdi + tls_address]
push [rax]
// save the TLS index
mov [rax], IMM32(tls_value)
// restore compressed data overwritten by the TLS index
push rax
section PEMAIN02
push rdi
section PEMAIN03
|
涉及到重定位的放在了一起:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
// =============
// ============= RELOCATION
// =============
section PERELOC1
lea rdi, [rsi + start_of_relocs]
section PERELOC2
add rdi, 4
section PERELOC3
lea rbx, [rsi - 4]
reloc_main:
xor eax, eax
mov al, [rdi]
inc rdi
or eax, eax
jz
SHORT
(reloc_endx)
cmp al, 0xEF
ja reloc_fx
reloc_add:
add rbx, rax
mov rax, [rbx]
bswap rax
add rax, rsi
mov [rbx], rax
jmp reloc_main
reloc_fx:
and al, 0x0F
shl eax, 16
mov ax, [rdi]
add rdi, 2
section REL64BIG
or eax, eax
jnz
SHORT
(reloc_add)
mov eax, [rdi]
add rdi, 4
section RELOC64J
jmp
SHORT
(reloc_add)
reloc_endx:
|
修改PEMAIN01字段的代码就会修改加壳后的入口函数汇编代码,注意栈对齐:
总结
本文主要是自顶向下分析整个upx打包流程中涉及的源码,在行文过程中学习到了很多知识,也可能存在疏漏,如有问题希望可以多多指出。
参考链接
更多【UPX 4.0.2 源码分析】相关视频教程:www.yxfzedu.com
相关文章推荐
- 编程技术-驱动保护-EAC内核调试检测分析 - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- Android安全-Android 系统源码下载编译刷机 - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- Android安全-编译frida16.0.2 python 模块 - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- 软件逆向-DASCTF X GFCTF 2022十月挑战赛 cuteRE WriteUp - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- Android安全-攻防世界Mobile通关记录_apk逆向12_RememberOther_Ph0en1x-100_ill-intentions_wp - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- 编程技术- 驱动开发:内核运用LoadImage屏蔽驱动 - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- 软件逆向-wibu证书 - 安全证书(一) - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- 二进制漏洞-CVE-2018-17463详细分析及复现 - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- CTF对抗-2022秋季赛题目提交 - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- Android安全-某当网apk加固脱个so - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- 软件逆向-360ini.dll注入explorer技术分析 - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- 二进制漏洞-CVE-2022-23613复现与漏洞利用可能性尝试 - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- 编程技术-过EAC HV检测 - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- 智能设备-Qiling框架模拟运行固件配合IDA动态调试 - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- 编程技术- 驱动开发:内核枚举进程与线程ObCall回调 - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- 编程技术-AVL/红黑树 C++ 递归实现/非递归实现 源码+视频教程 - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- Android安全-Frida编译2022 - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- 软件逆向-Windows 下的逆向分析-实战1 - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- 二进制漏洞-libFuzzer使用总结教程 - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
- 智能设备-一个简单的STM32固件分析 - 游戏逆向 游戏开发 编程技术 加壳脱壳
2):严禁色情、血腥、暴力
3):严禁发布任何形式的广告贴
4):严禁发表关于中国的政治类话题
5):严格遵守中国互联网法律法规
6):有侵权,疑问可发邮件至service@yxfzedu.com
接各种驱动定制如:游戏读写驱动,软件内存保护,防止调试等功能定制。
出租读写驱动,调试驱动,无痕注入支持各种游戏。
邮箱:service@yxfzedu.com
QQ:851920120
特别说明:不接游戏数据分析,外挂编写,登陆协议等类似业务。
